Metoidioplasty Surgery Procedures
Comparing Simple Release, Ring Meta and Belgrade Metoidioplasty Techniques
Metoidioplasty surgery is a gender-affirming procedure for transmasculine people that was developed in the 1980s an alternative to Phalloplasty. Metoidioplasty uses the tissue from the clitoris (which is analogous to the penis) to create a neophallus, or "new penis". Metoidioplasty is a good option for those with sufficient clitoral growth from use of testosterone. It's a less invasive and more affordable surgery than Phalloplasty. The average penis size from a "Meta" is 1.5-2 inches. Metoidioplasty results will depend greatly on surgical technique, surgeon experience, anatomy and genital enlargement from testosterone.

Metoidioplasty Result
Source: gires.org.uk
There are a few different Metoidioplasty techniques to choose from based on your needs. All Metoidioplasty surgeries include releasing the labial tissues surrounding the clitoris, and in some cases the suspensory ligament, to straighten and reposition the clitoris in a more forward position, to more closely approximate the position of a penis. Additional length of up to 50% can be achieved. The labia minora can also be used as flaps to provide additional girth.
Additional complimentary procedures are optional, including Vaginectomy, Urethroplasty, Scrotoplasty and Testicular Implants, and Mons Resection. Typical operating time for Metoidioplasty surgery is 3-5 hours and may require revisions in later stages.
If you're on the fence about Metoidioplasty vs. Phalloplasty, note that you can have Phalloplasty after Metoidioplasty. In fact, some surgeons perform Metoidioplasty as the first stage of Phalloplasty.
The Historical Development of Metoidioplasty Techniques
The first report of using the clitoris in male genital reconstruction was in 1973.
The Genitalplasty technique was developed by Dr. Michael Brownstein, who for 35 years was one of only a handful of surgeons in the United States who would perform Top Surgery. Dr. Brownstein had also devised a female-to-male genital procedure that he called Genitalplasty, which is a generic term that simply refers to plastic surgery of the genitals. In 1986, American author and transgender activist Lou Sullivan became Dr. Brownstein's second Genitoplasty patient. Little is known about the technique as Dr. Brownstein never published about it.
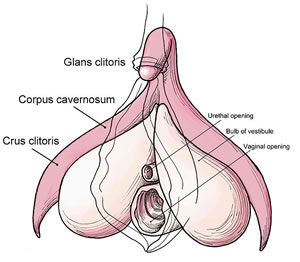
The Laub technique was the original version of what is now referred to as Simple Release or Simple Meta. It involved only the release of the clitoris. The term "Metoidioplasty" was first introduced in 1989 by Lebovic and Laub, originally from the Greek words "meta" (change), "aidion" (male genitalia), and "plasty" (formation).
The Hage technique was the first modern Metoidioplasty method to be described in medical literature, in 1996. It combined Laub's clitoral release and Bouman's urethral construction techniques to create an alternative to Phalloplasty. All patients received testosterone therapy for a minimum of 1.75 years prior to surgery, and had Hysterectomy completed before or during Metoidioplasty. This technique refined existing hypospadias repair surgeries, using local tissue rearrangements from the vaginal wall, release of the clitoral shaft and creation of the neourethra.
The Ring Metoidioplasty technique was developed in Japan by Dr. Ako Takamatsu to account for cases of poor development of the labia minora, clitoral body, or narrow vagina which made it difficult to obtain a sufficient length or diameter of the neourethra, resulting in high rates of fistula and stricture. The labial ring flap has a larger surface for neourethral construction. While Ring Metoidioplasty doesn't normally include Vaginectomy, the vaginal opening is narrowed to about the diameter of the little finger.
The Belgrade Metoidioplasty technique, or Full Metoidioplasty, is a single-stage procedure developed in Serbia which now serves as the basis for most "full" Metoidioplasty surgeries. It includes Vaginectomy as the first step, where all vaginal mucosa, except for part of the ventral wall, is removed. The chordee and clitoral ligaments are released to straighten and lengthen the clitoris. Urethral lengthening uses a combination of vaginal wall tissue, buccal mucosa (inner cheek) graft and labia minora flaps. Scrotoplasty is performed by joining two labia minora flaps at the midline and inserting testicular implants. This method creates a bifid scrotum, in contrast to Hoebeke's technique (aka. VY Scrotoplasty). Later refinements to the technique added a pre-operative step to optimize clitoral enlargement using dihydrotestosterone topical gel in combination with vacuum/pump device.
The Extensive Metoidioplasty technique was developed by Dr. Shahryar Cohanzad to enhance the masculine-appearance than that of previous techniques. To provide additional length, the technique includes extensive dissection of the crura to near-total detachment from the pubic bone. The labia minora are tubularized to create the neourethra, but connection to the native urethra is delayed until stage two. Patients are fitted for a penile traction device that is used post-operatively for at least a year.
Complimentary Procedures
Scrotoplasty and Testicular Implants
The most widely used technique for creating the scrotum is Hoebeke's technique, which was first described by Professor Piet Hoebeke, a urologist at Ghent University Hospital in Belgium. In the trans community, this is more commonly referred to as "VY Scrotoplasty" because the technique uses a V-Y advancement flap, where a V-shaped incision is made, the broad base of the V is advanced into the defect, and the defect is closed primarily in a Y-shape.
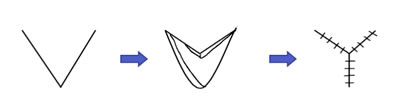
With Hoebeke's technique, bilateral labial flaps are dissected, rotated and advanced to create a single sac scrotum that is positioned in front of the legs, offering a better cosmetic result compared to earlier techniques. Incisions are made in each side of the scrotum, pockets are created and testicular implants are put in. Expanders may be used to stretch the tissues prior to placement of implants. This adds an extra surgery stage but creates a bigger scrotum that can accommodate larger testicular implants.
View 3D drawings of VY Scrotoplasty »
Urethroplasty / Urethral Lengthening
Another option with Metoidioplasty is Urethroplasty or Urethral Lengthening. Techniques vary (ie. anterior vaginal wall flap vs. buccal mucosa flap) but the results are the same: extension of the urethra from the native urethral opening to the tip of the penis so that the patient can urinate in a standing position. A catheter is placed inside the new urethra for 2-3 weeks while the neourethra heals.
Vaginectomy
Vaginectomy is an umbrella term referring to surgery procedures that remove all or part of the vagina and close the vaginal opening (Perineoplasty). A common misconception about Vaginectomy is that it completely removes the vagina, but this is very rarely done as a gender-affirming procedure. Complete Vaginectomy is typically reserved for cancer patients. In the context of FTM surgery, Vaginectomy is a Colpectomy (removal of the vaginal lining or epithelium) plus a Colpocleisis (fusion of the vaginal walls, which creates support for pelvic organs). Some surgeons require Vaginectomy with Metoidioplasty if Urethroplasty is being performed. Read more about Vaginectomy »
Mons Resection
A Mons Resection is a plastic surgery procedure that removes excess skin and fat from the pubic mound to allow the penis and scrotum to be moved to a more forward position, improving the aesthetics of the final Metoidiolpasty result.
Comparing Types of Metoidioplasty Surgery
| Procedure | Simple Release or Simple Meta |
Ring Metoidioplasty | Full Metoidioplasty | Centurion Metoidioplasty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clitoral Release | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Vaginectomy | N | N - Partial Closure | Y | Y |
| Clitoral lengthening | N | Y | Y | Y |
| Clitoral girth augmentation | N | N | Optional | Y |
| Urethroplasty | N | Y | Y | Y |
| Scrotoplasty | Optional | Y | Y | Y |
| Testicular implants | Optional | Y | Y | Y |
Pros, Cons, and Risks of Metoidioplasty
PROS: Natal-appearing penis, erogenous sensation, unassisted erections, easily concealed scars, shorter operative time, shorter recovery time, less invasive and expensive compared to Phalloplasty.
CONS: Small sized penis, good clitoral growth required, typically does not produce a bulge, scrotum can have bifid appearance (unless VY technique is used), even if urethroplasty is performed the patient may not be able to urinate standing up due to small penis size.
RISKS: Fistula (hole) or stricture (blockage) with urethroplasty, migration and/or extrusion of testicular implants. There are fewer risks associated with the Simple Meta procedure since urethroplasty is not performed.
Requirements for Metoidioplasty
Basic health requirements:
- Good physical and mental health
- 18 years or older
WPATH Standards of Care requirements:
- Pre-operative psychological counseling and two letters of support
- Hormone therapy, miminum of 2 years for best Metoidioplasty results. If one stops taking testosterone, the neophallus can shrink in size.
- Minimum of 1 year of real life experience (RLE)
Each surgeon may have their own specific requirements in addition to these.
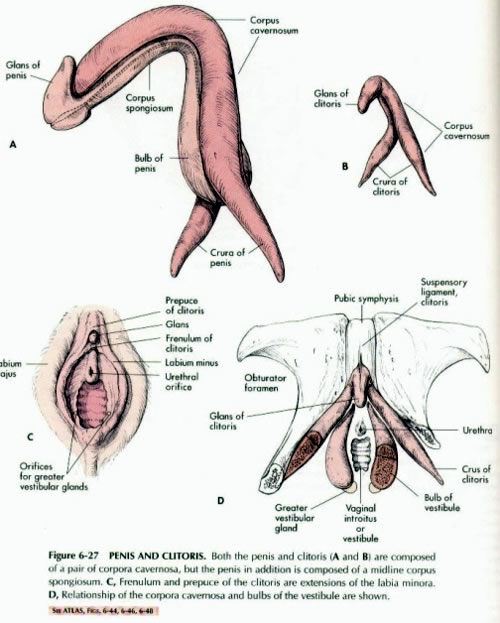
Comparing Penis Tissues to Clitoral Tissues
Last updated: 11/16/21